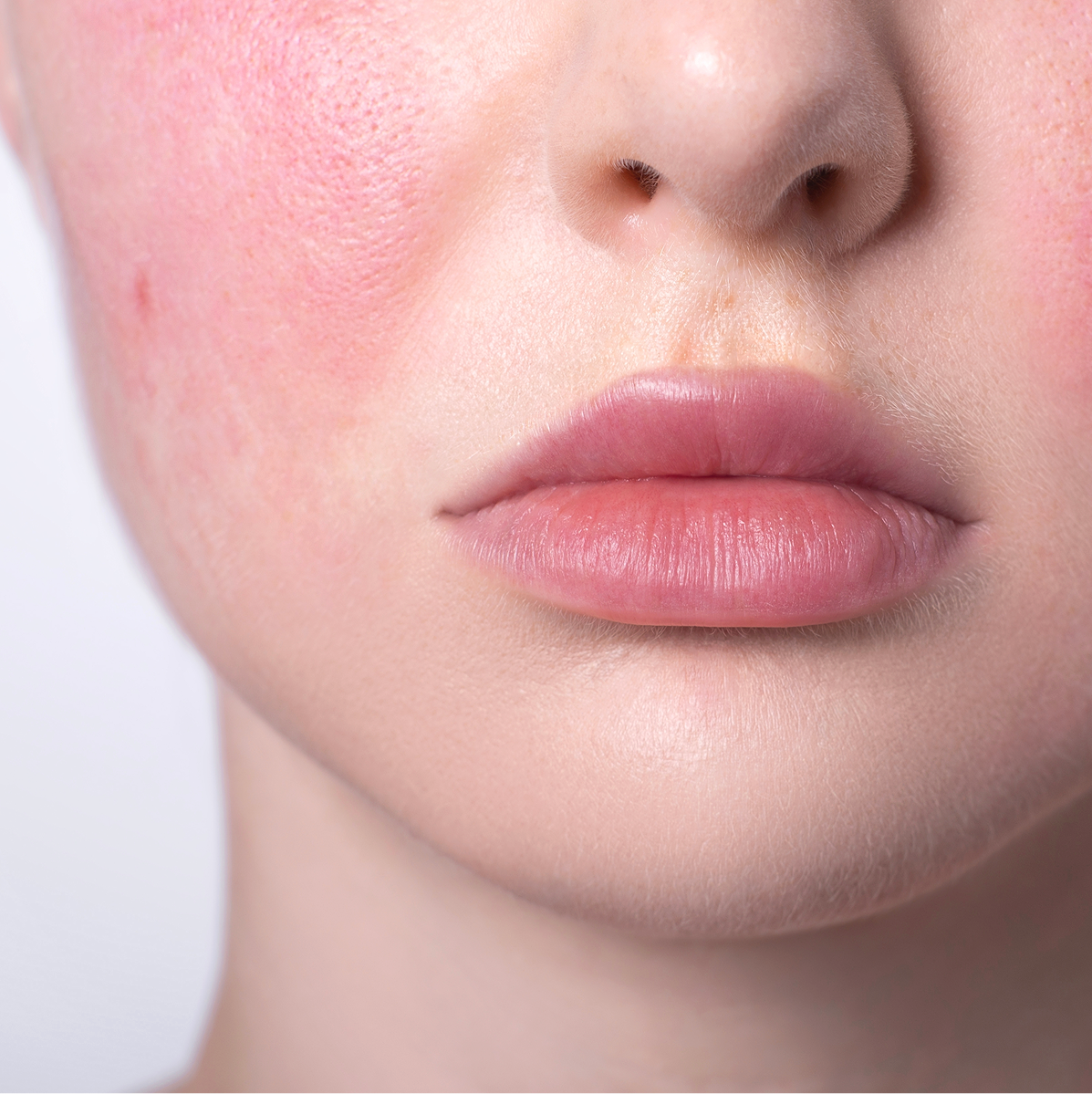
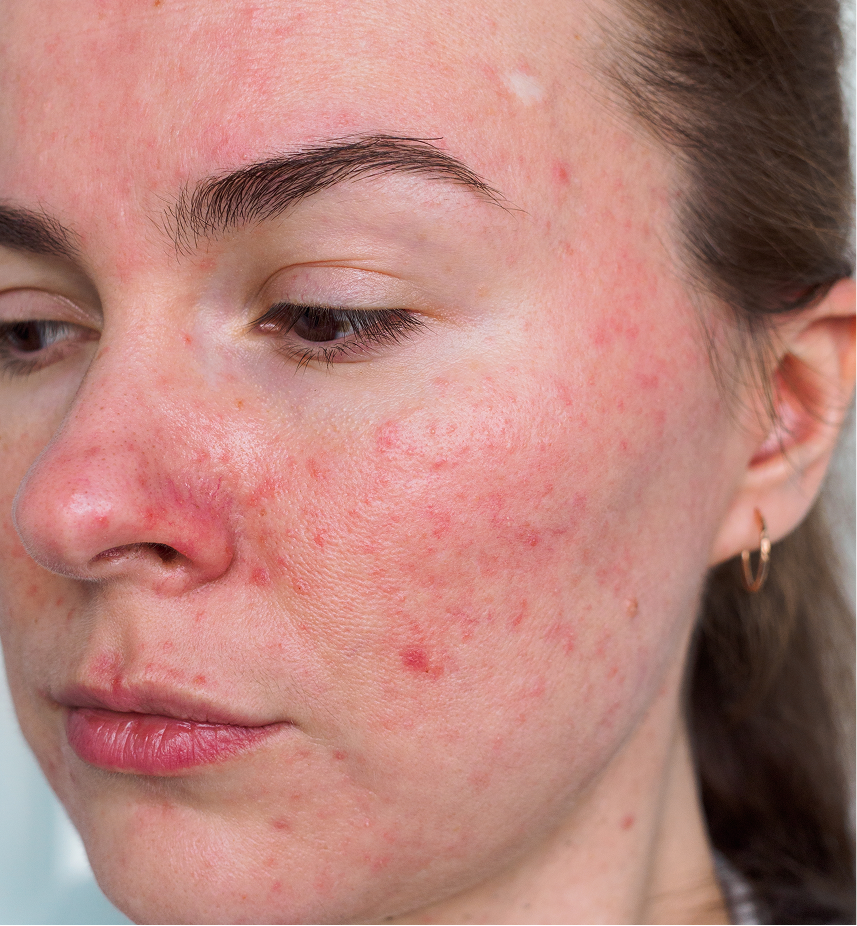
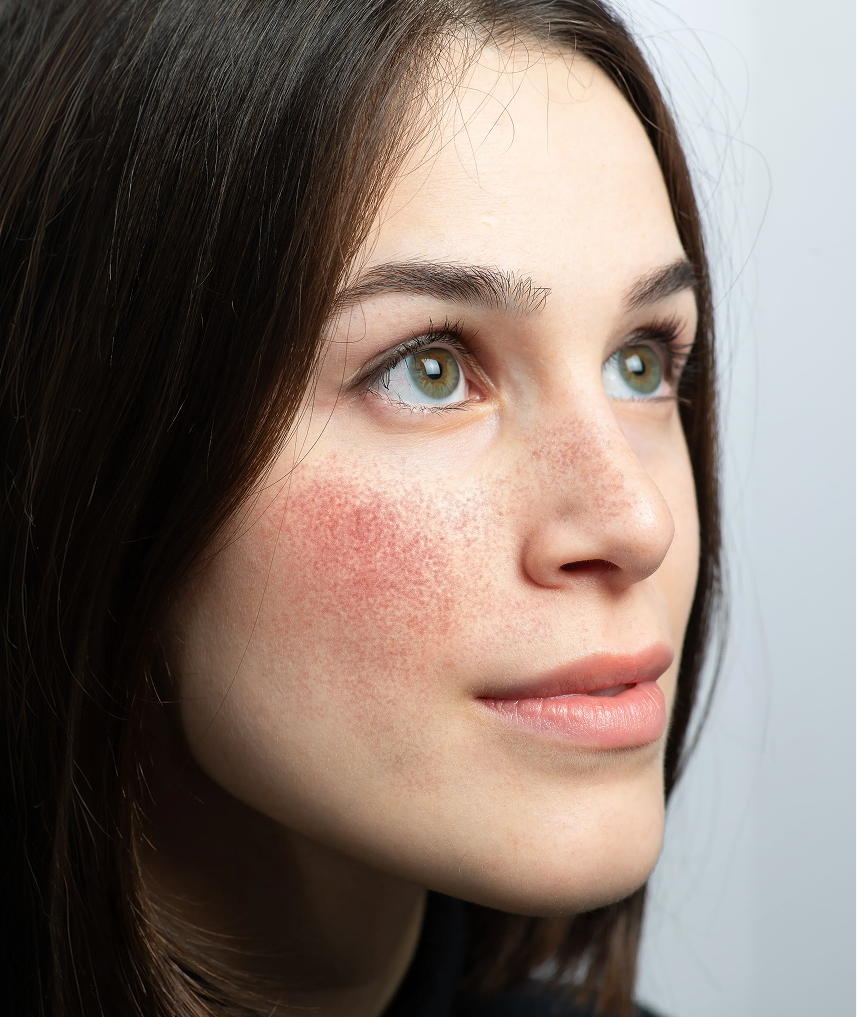
Rosacea is a common and chronic skin disorder characterized by redness, flushing, and acne-like lesions on the face. Occasionally, it can affect the eyes, causing redness and eye irritation.
People with fair skin are most commonly affected by rosacea, but it can occur in any skin type. Most often, rosacea is an adult-onset condition, with most cases occurring in adults over 30. However, the condition can also appear in adolescence or childhood.
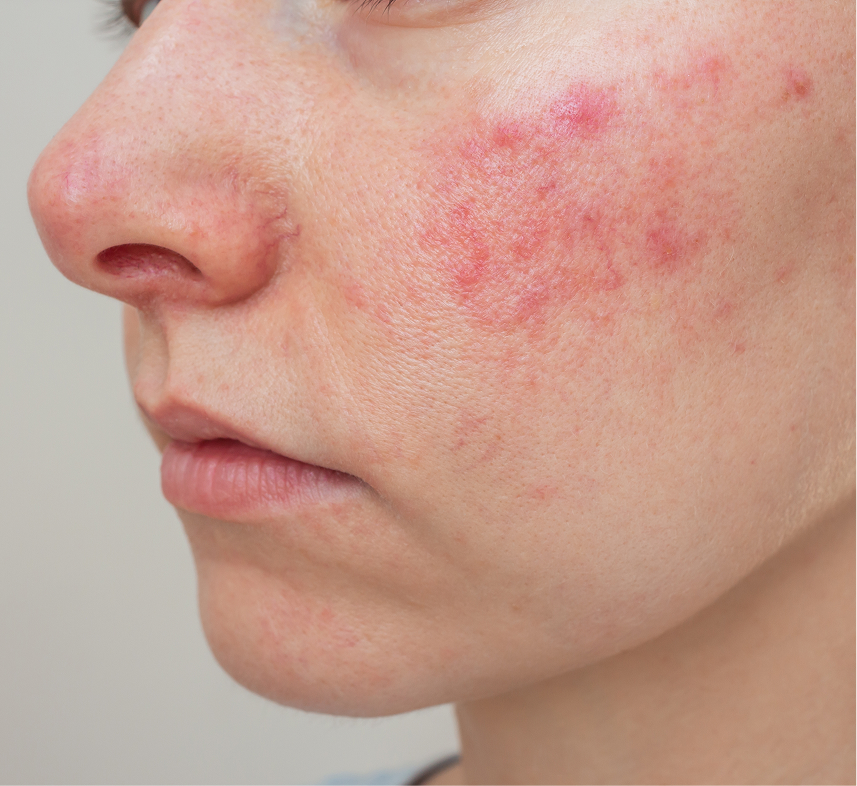

Triggers for rosacea vary based on the individual, but common triggers include extremes of temperature, sunlight, spicy foods, alcohol, chocolate, exercise, emotions, medications, and hot beverages. Paying attention to what triggers your rosacea is important for managing it over time. It is recommended to avoid triggers when possible, but not all can be avoided.
Rosacea can affect a wide range of people, but certain signs and risk factors indicate that professional treatment may be beneficial. Individuals with oily skin, enlarged pores, or a tendency toward acne-like breakouts may be more prone to rosacea flare-ups. Genetic and environmental factors – such as sun exposure, stress, or extreme temperatures – can trigger or worsen symptoms. Visible enlarged blood vessels, persistent red bumps, and other physical symptoms of rosacea can indicate the need for intervention. Those experiencing frequent flare-ups, discomfort, or severe rosacea should consider consulting a specialist to develop a personalized management plan that addresses both appearance and underlying triggers.